Rivers have always played a life-giving role in the world. Found on every continent, they supply food, water and are home to wildlife.
Rivers are also the foundation of civilisations. Major cities such as Kuala Lumpur, New York City, London, Calcutta and Shanghai were founded around rivers, which provided routes for transportation, trade and exploration.
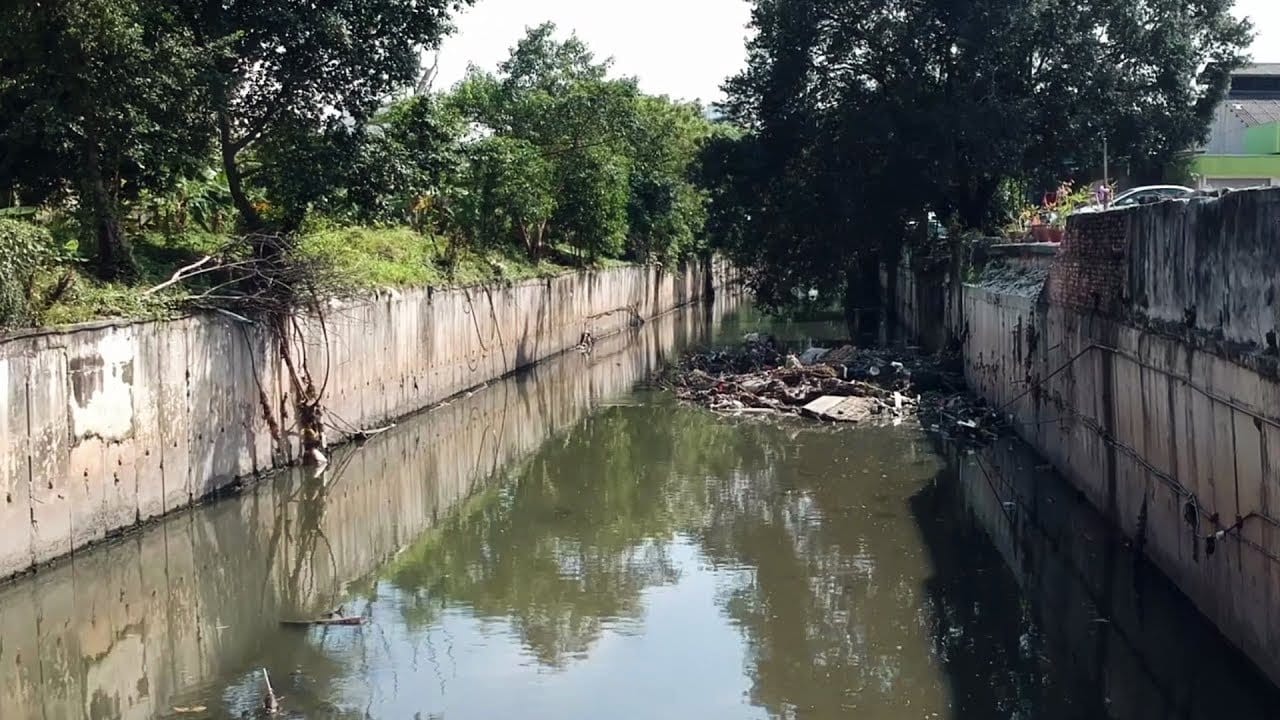
But rivers have also borne the brunt of development. Growing populations, pressures of land management and poor waste management have reduced many of them to waste dumping grounds. Having lost their usefulness, polluted rivers end up being covered up or hidden away from society.
Breathing new life into the Bandar Sunway canal
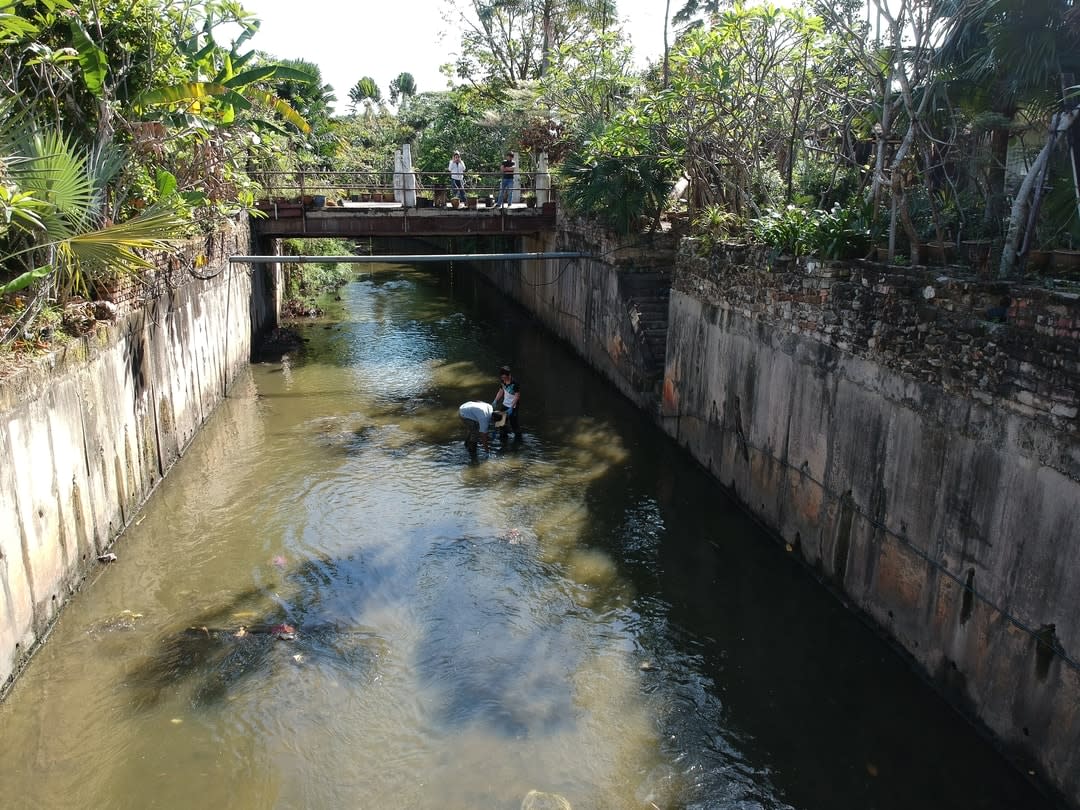

Bandar Sunway, or Sunway City, is a township in Subang Jaya, Malaysia. It rose from an 800-acre mining wasteland in the 1980s to become a thriving township and model of sustainability aligned to the United Nation's sustainable development goals. More than 25,000 trees have been planted and more than 150 species of flora and fauna have blossomed as it has transformed from the depths of a mining crater.
It also has its own canal, which is often mistaken for a monsoon drain. Canals are artificial waterways or artificially improved rivers.
Originally a river flowing from Kelana Lake, the 6km-long canal measures 5m wide, and runs through the Greater Kuala Lumpur Petaling District before discharging into the Klang River.
“The original river cuts across three municipalities, with some sections owned by Bandar Sunway and some owned by its neighbouring municipalities,” said Professor Khu Soon-Thiam, Head of Civil Engineering at Monash University Malaysia’s School of Engineering.
“You can see the natural riverbank with vegetation upstream. Moving downstream from Federal Highway past Sunway-Monash Residence, the five-metre-wide canal then reverts to the original river past the residence.”
Over the past few decades the river has changed its course.
“Based on old maps, we found that the river follows a different path today,” Professor Khu said. “Rivers can move either in their natural environment or due to human intervention such as the construction of the Federal Highway. Back then, there was no golf course.” he explained.
In January 2018, Khu and his team at Monash Malaysia started the Bandar Sunway ‘River of Sustainability’ project to rehabilitate the Bandar Sunway canal. They hope to improve citizens’ quality of life and increase the economic value of the properties surrounding it.
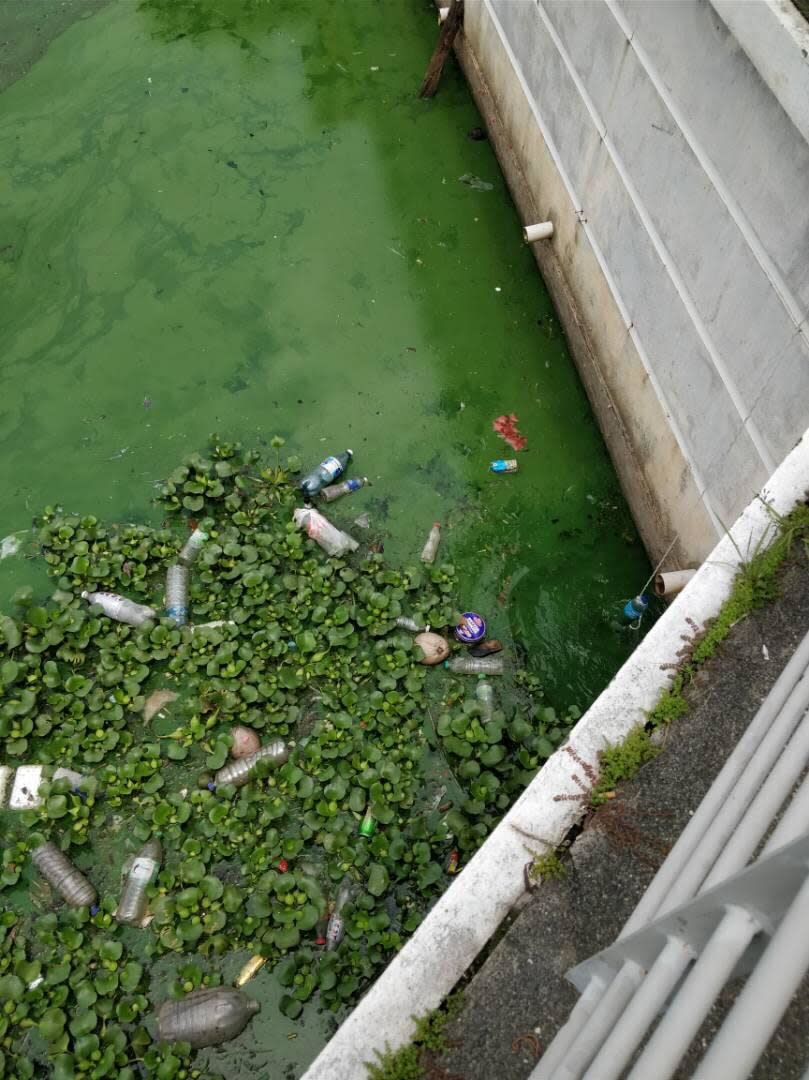
He described the river as polluted and unsafe for recreational use.
“People appreciate the natural environment. Whenever they have free time, they will hike or go for nature walks. It’s sad that we have a water body here that people are unaware of, and also unable to make full use of due to its current state,” he said.
River rehabilitation
Unique to the ‘River of Sustainability’ project is its multi-disciplinary approach, combining the expertise of Monash University’s different disciplines — civil and chemical engineering, biochemistry, biology, business and social science — to achieve the project’s objectives.

“Unlike the ‘River of Life’ project in Kuala Lumpur, the ‘River of Sustainability’ project goes beyond beautification and economic objectives. We are also looking at it from a sustainability perspective, communicating with stakeholders from the beginning and throughout the project, and quantifying the health impact of the river on people,” he said.
Using innovative molecular bioscience-based tools such as the ‘DNA recovery technique’, the research team was able to track bacterial and viral contamination found in the water and pinpoint the source of pollution.
The team will then employ nature-based solutions such as a stepped cascade and bio-filtration system to enhance the water quality of the canal and prevent pollution. Nature-based solutions are green infrastructure that can substitute or work together with man-made infrastructure in a cost-effective manner.
“Currently, we’re approaching Sunway Group to ascertain the costs of the structural measures, after which we will talk to the Subang Jaya Municipal Council (MPSJ) for further discussion. We are also looking at non-structural measures such as developing policies and educational materials,” he said.
Hope for future restoration efforts
It is Khu’s hope that restoring the Bandar Sunway canal will inspire others to care for their local rivers.
“We want to demonstrate that it is possible to turn a canal or river that has degraded and rehabilitate it. We hope that as more people are made aware of our efforts, they will begin to ask about the rivers in their backyards and replicate the restoration efforts,” he said.
Khu is also involved in the Sunway South Quay Lake Water Quality Improvement project, with a RM100,000 grant from Sunway Properties and Facilities Management. He has also been awarded a €103,000 (RM482,371) grant from the European Union Horizon 2020, which is the EU’s Research and Innovation Programme.
“We are looking at the same idea [rehabilitating rivers] but to be implemented in Iskandar Johor. We are working together with Monash University’s Clayton campus in Australia to see what we can learn from Europe, Australia and Malaysia, and integrating that knowledge for implementation,” he said.
Find out more about this topic and study opportunities at the Graduate Study Expo