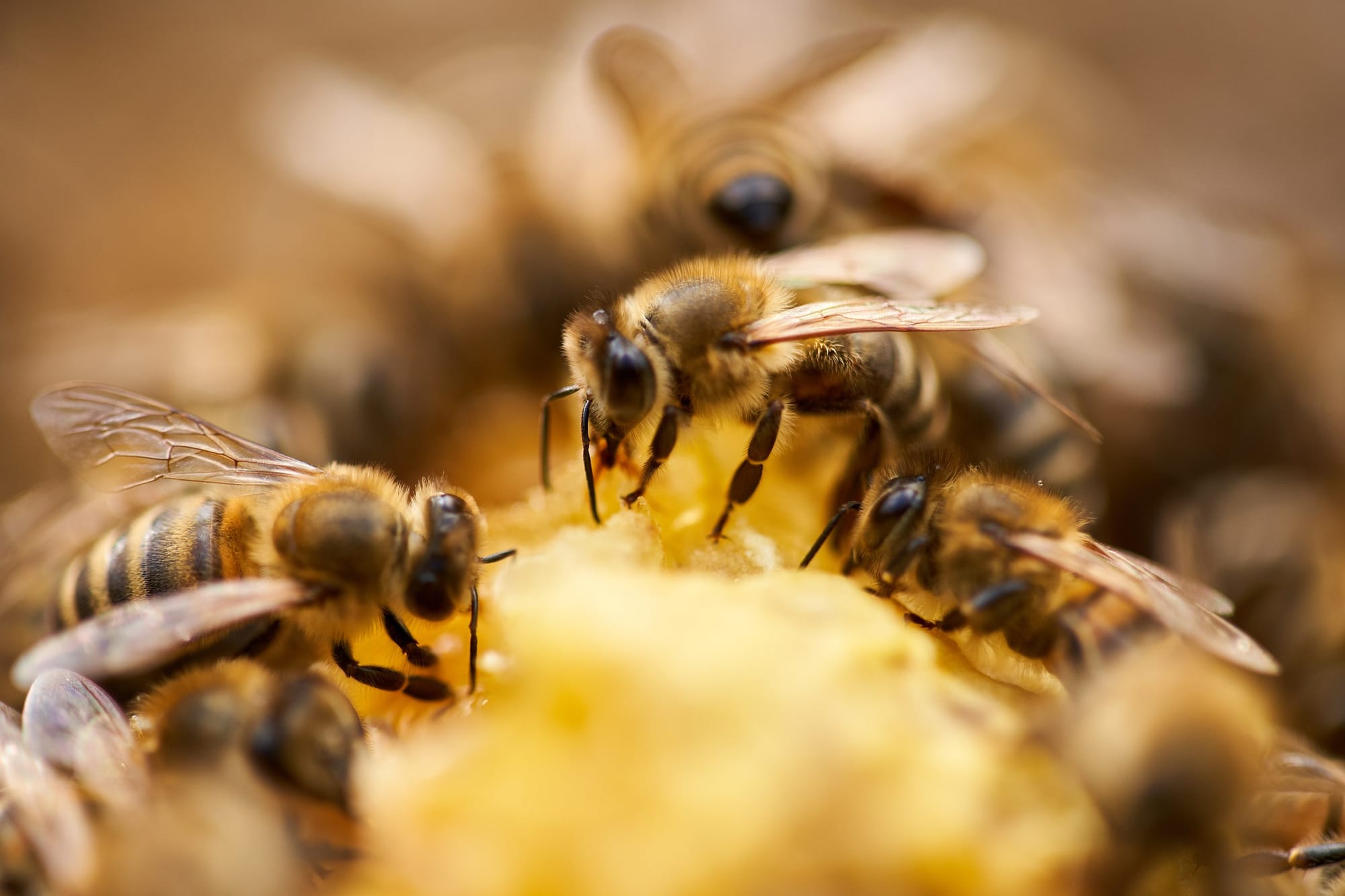
Honey can be found in most households as a sweetener or flavouring agent. Besides being nutritious, it’s also packed with antioxidants and medicinal properties. For centuries, honey has been a natural remedy for various ailments, including throat infections and wound healing.
Besides honey, bees also produce other beneficial substances such as royal jelly, bee bread (pictured), bee pollen, and propolis.
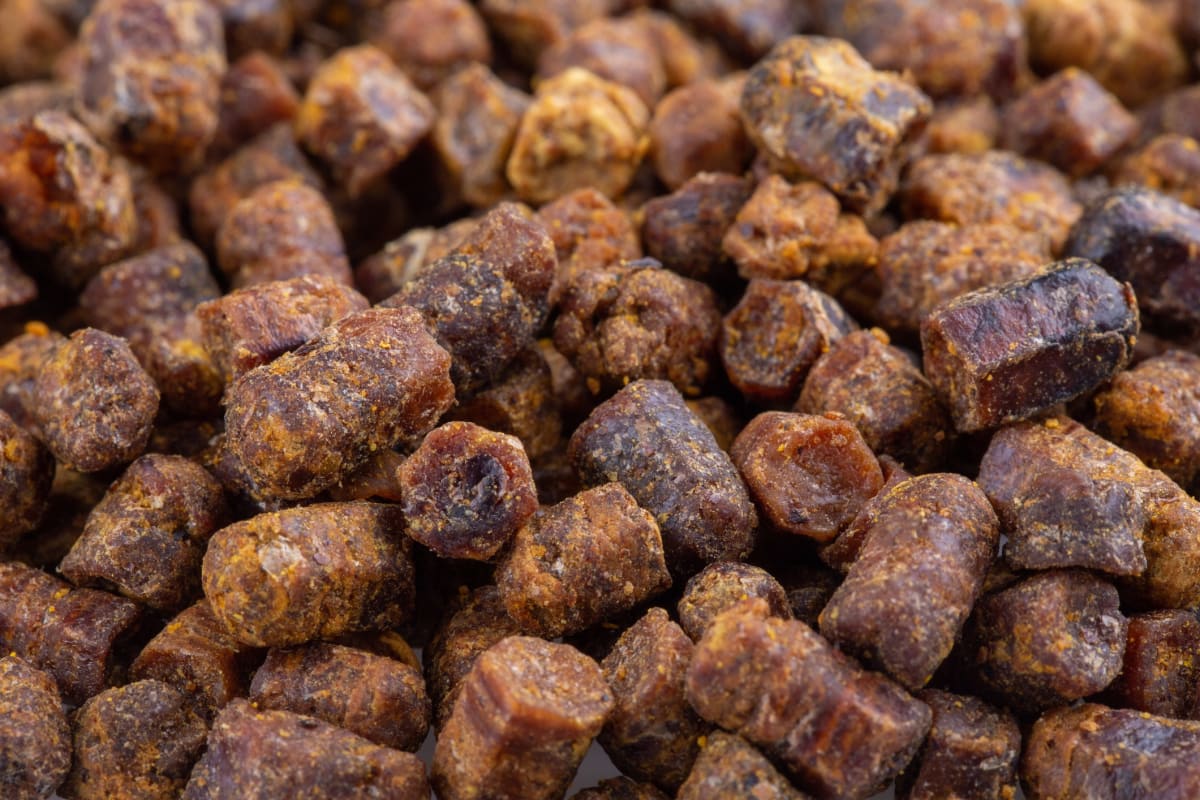

Propolis is a resinous substance collected by bees from tree buds and used to line the hives and protect the colony against disease and infection.
It’s been used for its antibacterial, antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties in traditional medicine, and has been studied for its potential health benefits, including its use as a dietary supplement.
Propolis has been shown to have hepatoprotective, anti-tumour, antioxidative, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Although more than 300 constituents have been identified in propolis in the past few years, these functional properties are mainly ascribed to only a few substances – polyphenols of flavonoids, phenolic acids and their esters, of which flavonoids, in particular, are considered the top contributors.
However, propolis in its raw form is difficult to use due to its poor solubility in water, susceptibility to oxidation, low bioavailability, and short shelf-life, limiting its application for human consumption unless extracted and formulated.
Not realising its true potential, many bee farmers discard propolis, and harvest only honey for commercial purposes. This is a wasted opportunity considering propolis’ potent medicinal value.
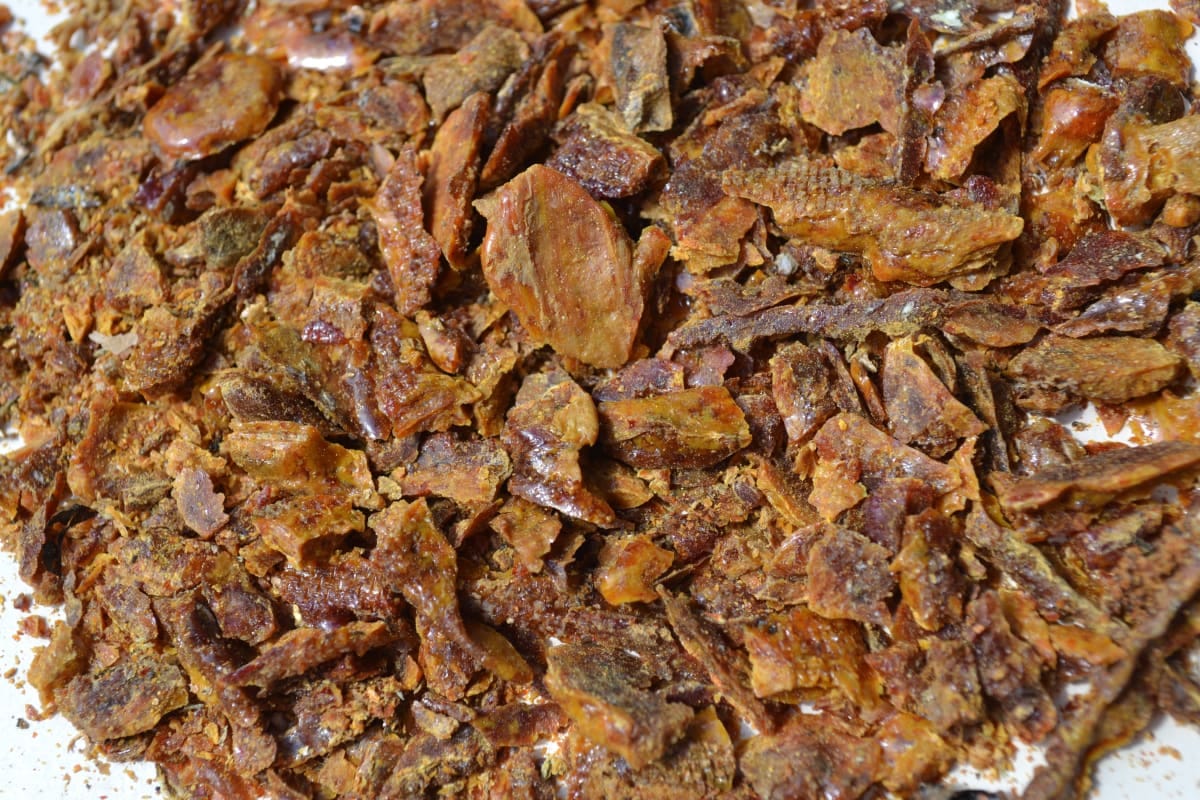

A research team from Monash University Malaysia’s School of Pharmacy took up the challenge to produce the first liquid formulation for stingless bee propolis.
The team included Dr Ronald Lee, Kashif Maroof, Associate Professor Goh Bey Hing and Associate Professor Siow Lee Fong, led by Professor Gan Siew Hua.
Propolis was extracted using supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), which is environmentally-friendly due to the use of green solvents. The method operates at a low temperature, thereby retaining valuable heat-sensitive compounds.
In addition, it’s highly selective, yielding purer extraction. The product was formulated into a lipid-based delivery system with pharmaceutical-grade lipids and surfactants forming a golden-yellow solution.
Read more: The sweet science of honey: Exploring the health benefits
The product has minimal impact on the environment. It’s deemed a waste of wealth, since propolis is usually considered a “waste” and is being repurposed as a health supplement. The production used recyclable packaging materials such as glass, paper and rubber, but even the dropper bottles can be repurposed.
Called “Malaysian Kelulut Golden Propolis”, the team exhibited the product at the International Invention, Innovation and Technology Exhibition (ITEX) 2022, winning a silver medal.
The product can be a natural ingredient for cosmetics and personal care products (such as hand soap, shampoo, toothpaste, mouth spray, throat spray, mouthwash, and creams), and helps to reduce reliance on synthetic compounds.
The research team received additional funding from a government grant, the Private Public Research Network (PPRN), for further development of stable propolis-based powders. The powders have the potential to be formulated into tablets, capsules or sachets.